“Major Barber was declared rebel”
On Monday, 19 Sept 1774, the Fleet brothers’ Boston Evening-Post reprinted the article from the New-York Gazetteer that I’ve been discussing, listing eighteen Boston men as “authors” of rebellion in Massachusetts.
That article took the form of a letter “To the Officers and Soldiers of his Majesty’s Troops at Boston.”
One obvious question is: Did those men get the message? Did that newspaper item have any effect?
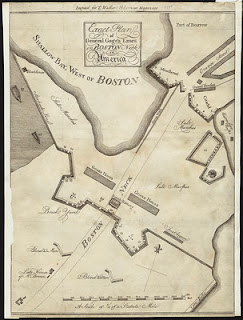
For an answer, I point to the 3 October Boston Gazette. It contained a long letter from Enoch Brown, who owned a house and store on the Boston Neck. On the map shown here, it’s the building with a label in the lower left corner.
Writing to Edes and Gill on 24 September, Brown detailed a dispute with the British army that he said started a week before.
(Army officers argued that the trouble started back during the “Powder Alarm,” and I may analyze that part of Brown’s letter sometime. For now, I’m confining myself to what happened on 17 September and afterward.)
Brown refused to sell rum to a British soldier that Saturday afternoon. The redcoat swore at him and, Brown said, “attempted to strike me with a large club.” Brown ran to the army camp to complain. He was told to speak to Lt. Col. George Maddison. Then came the Sabbath, and Brown finally met Maddison on Monday.
“Col. Maddison…received me with great politeness,” Brown stated. The soldier was already on trial for “getting drunk,” so the colonel added Brown’s accusation as another charge and asked him to return for the trial the next day.
On the morning of Tuesday, 20 September, Brown came back to the camp with two witnesses, William Shattuck and Nathaniel Barber, Jr. The proceeding didn’t go well for the locals. The officers trying the case believed they were rebels and the soldiers were justified in calling them that or worse. One officer
In between those two mornings, the Boston Evening-Post printed the item listing “Major Nathaniel Barber” among the leaders of rebellion in Boston. And the next day, army officers clearly knew his name.
TOMORROW: Nathaniel Barber to the end.
That article took the form of a letter “To the Officers and Soldiers of his Majesty’s Troops at Boston.”
One obvious question is: Did those men get the message? Did that newspaper item have any effect?
For an answer, I point to the 3 October Boston Gazette. It contained a long letter from Enoch Brown, who owned a house and store on the Boston Neck. On the map shown here, it’s the building with a label in the lower left corner.
Writing to Edes and Gill on 24 September, Brown detailed a dispute with the British army that he said started a week before.
(Army officers argued that the trouble started back during the “Powder Alarm,” and I may analyze that part of Brown’s letter sometime. For now, I’m confining myself to what happened on 17 September and afterward.)
Brown refused to sell rum to a British soldier that Saturday afternoon. The redcoat swore at him and, Brown said, “attempted to strike me with a large club.” Brown ran to the army camp to complain. He was told to speak to Lt. Col. George Maddison. Then came the Sabbath, and Brown finally met Maddison on Monday.
“Col. Maddison…received me with great politeness,” Brown stated. The soldier was already on trial for “getting drunk,” so the colonel added Brown’s accusation as another charge and asked him to return for the trial the next day.
On the morning of Tuesday, 20 September, Brown came back to the camp with two witnesses, William Shattuck and Nathaniel Barber, Jr. The proceeding didn’t go well for the locals. The officers trying the case believed they were rebels and the soldiers were justified in calling them that or worse. One officer
ask’d Mr. Barber whether there was not a man in town called Major Barber—Shattuck and Barber also described the presiding officer reprimanding Brown this way:
yes sir, replied Mr. Barber and he is my father——
The officer then said, that Major Barber was declared rebel, and told the son that he was doubtless tainted with the same principles, and therefore unworthy to be admitted as evidence against a soldier;
to which Mr. Barber replied that his father was an honest man, but be that as it might, he thought it extremely hard to be censur’d for his father’s conduct;
A very honest man indeed! return’d the officer
how dare you—you rascal! who are a rebel—have the impudence to come here to complain of a soldier, and bring for evidence the son of a declared rebel.Something appeared to have happened between Monday morning, when Lt. Col. Maddison was polite to Brown and took his accusation seriously, and Tuesday morning, when officers of the same regiment lambasted Brown and Barber as lying rebels.
In between those two mornings, the Boston Evening-Post printed the item listing “Major Nathaniel Barber” among the leaders of rebellion in Boston. And the next day, army officers clearly knew his name.
TOMORROW: Nathaniel Barber to the end.

No comments:
Post a Comment